ABOUT
Last Update...2021.12.15
RESEARCH TOPIC
The sun is actually constantly undergoing explosive and mass ejection phenomena on the solar surface.
In particular, sudden explosive phenomena are called solar flares.
Solar flares have a severe impact on the Earth's environment in the form of magnetic storms and radiation, and therefore understanding them is essential for our human civilization. Currently, we have not succeeded in predicting the occurrence of solar flares, so "When will it happen? How large a solar flare will occur?" are very important issues.
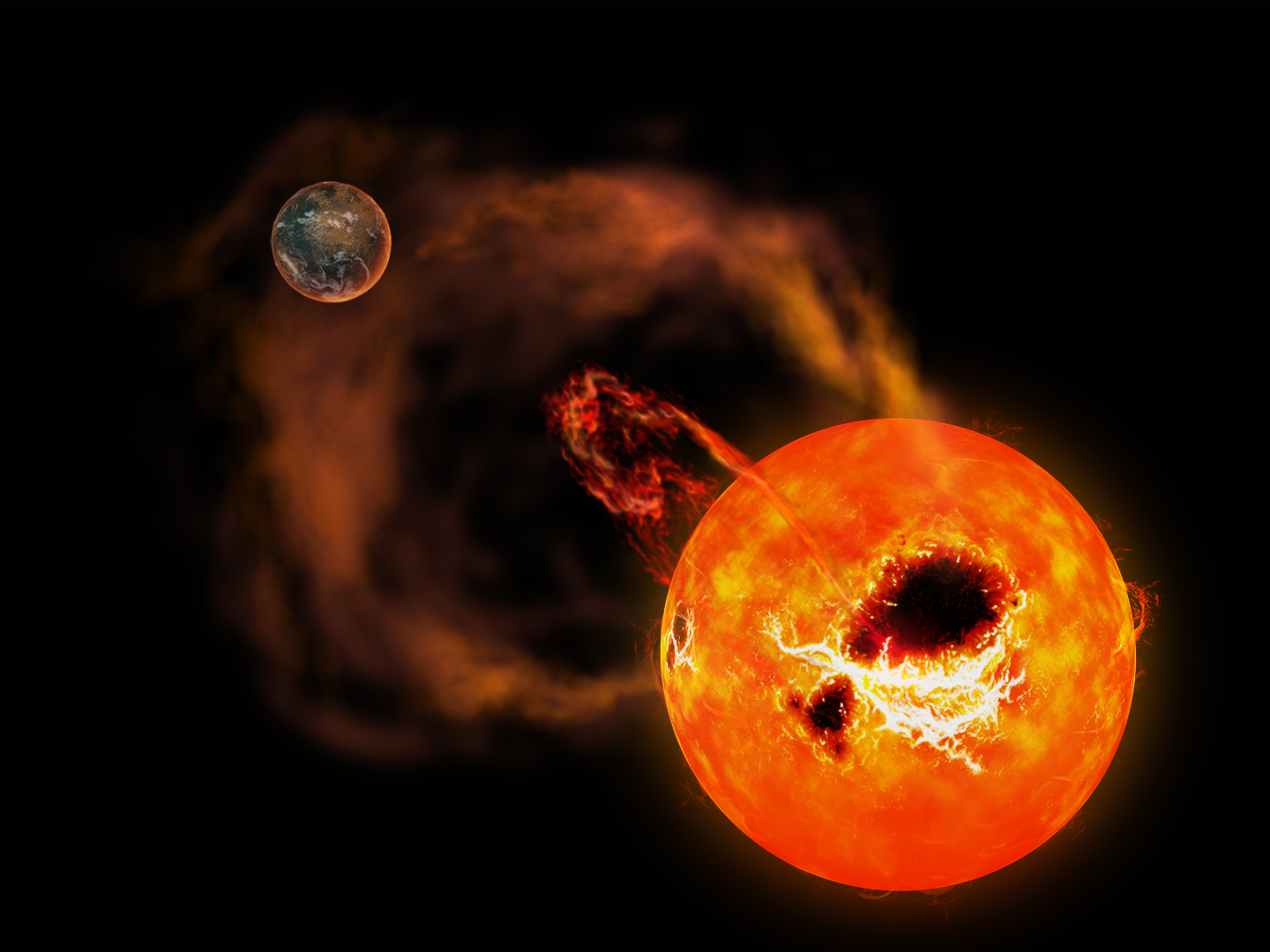
In 2012, it was discovered that stars very similar to our Sun (solar-type stars) actually experienced a "superflare," a flare 10-10,000 times larger than the largest solar flare in the history of solar observations. This discovery was a surprise to the world, as it had been believed in astronomy that such a superflare would not occur on the Sun. I have been asking myself questions such as, "Do superflares actually occur on the sun?" If so, "what will happen to the Earth?". I am conducting research to compare the Sun with such active Sun-like stars that cause these superflares.
So far, I have found observationally that the superflares of solar-type stars and the giant sunspots (huge magnetic energy blobs) that are essential to trigger them are produced by the same mechanism as the small-scale flares and spots of the Sun (Namekata et al. 2017b&c, 2019, 2020a).
Recently, we have also promoted research using the Kyoto University Seimei Telescope to obtain hints about the heating mechanism in M-type stellar superflares (Namekata et al. 2020b), and succeeded in the first detection of giant filament ejections associated with stellar superflares on young Sun-like stars (Namekata et al. 2021, Nature Astronomy). 2021, Nature Astronomy).
However, the study of superflares in solar-type stars has just begun and we need to continue our research in order to solve our ultimate questions.